Rotating radio transients (RRATs) are a subclass of pulsars characterized by sporadic emission. Up to now, although nearly 170 RRATs have been discovered, a large number of RRATs lack accurately measured rotation periods, and about two-thirds of RRATs do not have definite burst rate information due to the lack of follow-up observations. The physics responsible for the sporadic nature of the emission remains unclear due to the inherent difficulty in their detection.
Using the Parkes telescope, a postgraduate student from the Pulsar Research Group of the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, REN Xinhui, conducted an analysis of 10 RRATs. Eight of these RRATs were observed with the Ultra-Wideband Receiver (UWL).
The results were published in the Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics (RAA).
The researchers calculated that the burst rates of PSRs J1919+1745, J1909+0641, and J0628+0909 are 847 h-1 , 58h-1, and 60h-1, respectively. The pulsar spectral analysis software, pulsar_spectra was utilized for an in-depth broadband analysis of the average pulse and single pulse spectral characteristics for PSRs J1919+1745, J1909+0641, and J0628+0909.
The findings indicate that the majority of these spectra can be well fitted by a simple power-law model, featuring relatively flat spectral indices and a comparatively small scatter in single-pulse spectral indices, ranging from -3.5 to +0.5. For five additional RRATs observed with the UWL receiver, the researchers provided their fluence and flux density upper limits.
Furthermore, this research has, for the first time, reported the rotation period of PSR J1709-43 to be 0.897s, with a derivative of the rotation period recorded at 2.42*10-14s s-1.
The researchers have collected data for PSR J1649-4653 covering 11 years, with a total observation time of 10 hours. All the observations were carried out in the folded mode. Out of these, 65 observations (~51%) presented the burst pulse profiles.
However, the flux density of PSR J1649-4653 is found to be significantly weak, with a value of 0.14±0.02 mJy for the detectable pulse profiles.The analysis shows that PSRs J1919+1745, J1709-43 and J1649-4653 are potentially nulling pulsars or weak pulsars with sparse strong pulses.
By exploring the radiation characteristics and timing properties of RRATs, significant breakthroughs could be achieved in the study of RRATs, enhancing our understanding of the distribution of pulsars within the Milky Way. Additionally, this research may advance our knowledge of the likelihood of neutron star formation following supernova explosions.
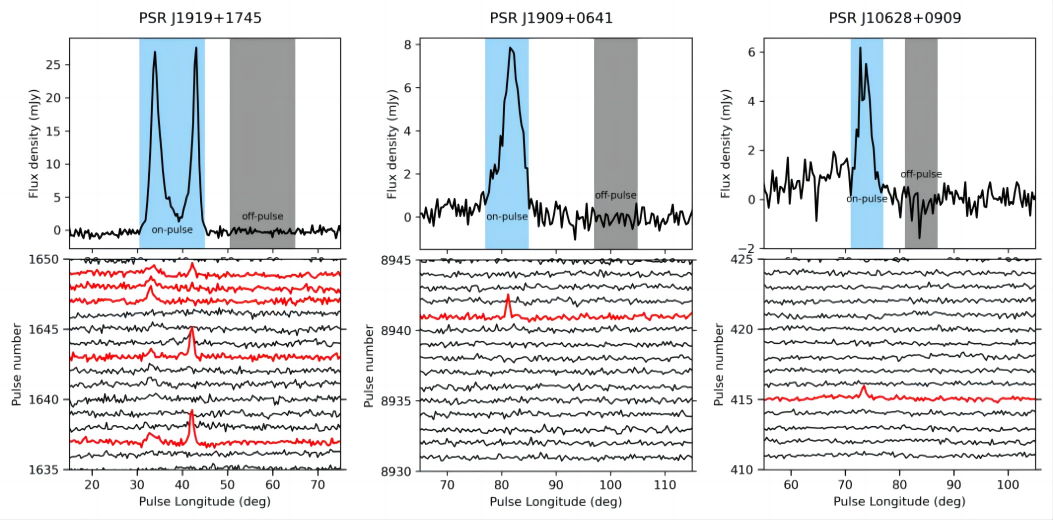
Figure. Integrated proflies and partial pulse sequences of 3 RRATs.
Contact: REN Xinhui
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: renxinhui@xao.ac.cn
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4527/ad2dbe