The world's most powerful steerable 110-meter radio telescope, also known as the QiTai radio Telescope (QTT), will be built by Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) over a period of six years, after its construction kicked off at the Qitai site of XAO.
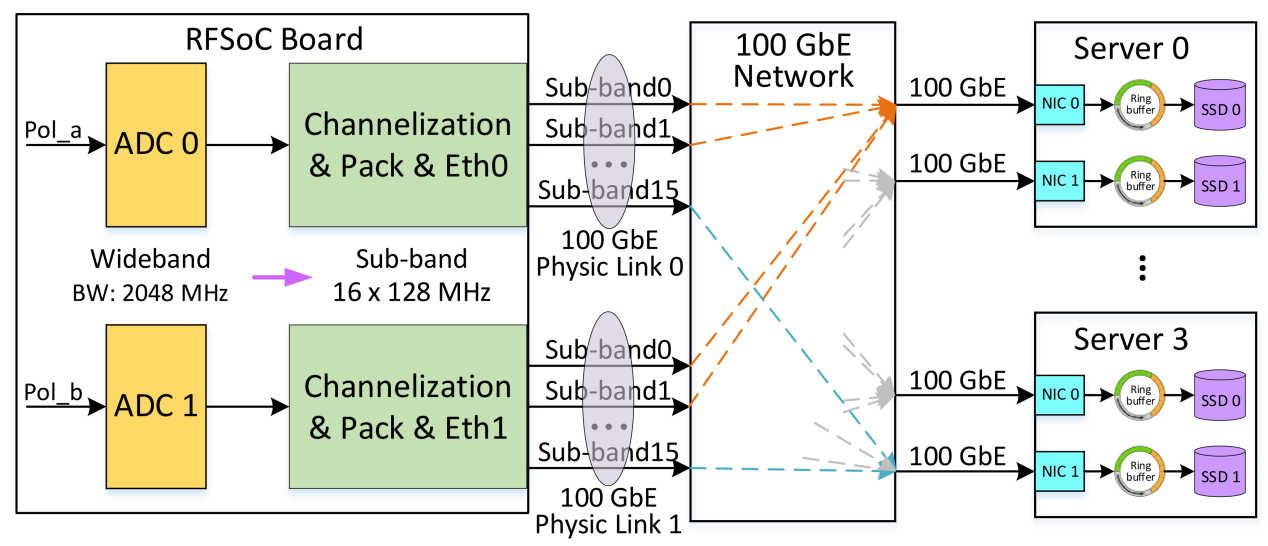
QTT will be equipped with Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) signal receiving and processing system. In order to upgrade the performance of the telescope, the engineers from the QTT signal receiving and processing team of XAO designed a new UWB signal acquisition and processing experimental system.
The results were published in Publications Of The Astronomical Society Of The Pacific on July 24.
The UWB system can improve the observation sensitivity of the telescope by increasing the bandwidth, but it also poses great challenges to signal acquisition, transmission and processing. In addition, the wider bandwidth will also incorporate more electromagnetic interference signals, which will affect the quality of astronomical observation and cause a saturation effect on the system.
In order to avoid the UWB signal phase and amplitude fluctuations caused by environmental and temperature changes in the analog transmission link, the new system uses a high-performance, low-power RFSoC circuit to directly sample the RF signal at the receiver end. In addition, the new signal acquisition circuit uses higher quantization accuracy to increase the dynamic range of the received signal, thus avoiding saturation caused by strong interference.
The researchers aimed to realize the real-time processing of UWB signals, so they divided the UWB signals into multiple digital sub-bands to implement, which are transmitted to the remote High-Performance Computer (HPC) cluster through 100 Gb high-speed digital fiber links for processing.
The system is more flexible and expandable, and its control program can configure the involved computing resources according to the observation bandwidth and computational complexity. Furthermore, each HPC node is configured with NVMe SSD cards for high-speed baseband data recording to realize raw astronomical information capture and adaptive RFI elimination.
To verify the actual observation effect of the system, the researchers deployed it on the Nanshan 26-meter radio telescope and conducted pulsar observation experiments. They found that the signal-to-noise ratio of the merged pulsar is obviously stronger than that of the unmerged single subband data, which indicates that the system is working as expected.
This work provides a high-performance and flexible solution for the design of QTT’s versatile UWB backends.