

Researchers certify seven large-amplitude δ Scuti stars
High-amplitude δ Scuti stars (HADS) are typical late A-type or early F-type pulsating stars, positioned at the intersection of the main sequence and the classical instability strip on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. These stars show pulsation periods ranging from 1 to 6 hours, with amplitude exceeding 0.3 magnitudes.
Recently, LV Chenglong, a PhD student from the Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and his collaborators successfully identified seven HADS stars with significant pulsation characteristics from over 59,000 δ Scuti stars using precise time-series photometric data from the TESS space telescope.
The results were published in The Astrophysical Journal on Dec 10.(2023,APJ,959,33)
The study utilized high-precision photometric data from the TESS space telescope, providing crucial information for certifying and understanding HADS pulsation characteristics. Through comprehensive analysis of light curves, period-luminosity relations, and period ratio diagrams, two radial pulsating HADS (TIC 30977864 and TIC 387379145) and a double-mode pulsating HADS (TIC 30977864) were confirmed, along with four other stars possibly exhibiting triple-mode pulsation.
In addition,researchers conducted a statistical analysis of the relationship between metallicity and pulsation period for 176 HADS stars. Future research will involve studying a larger sample of HADS stars by combining spectroscopic data, addressing ratio issues of the pulsation period, and providing stronger constraints to build precise stellar models.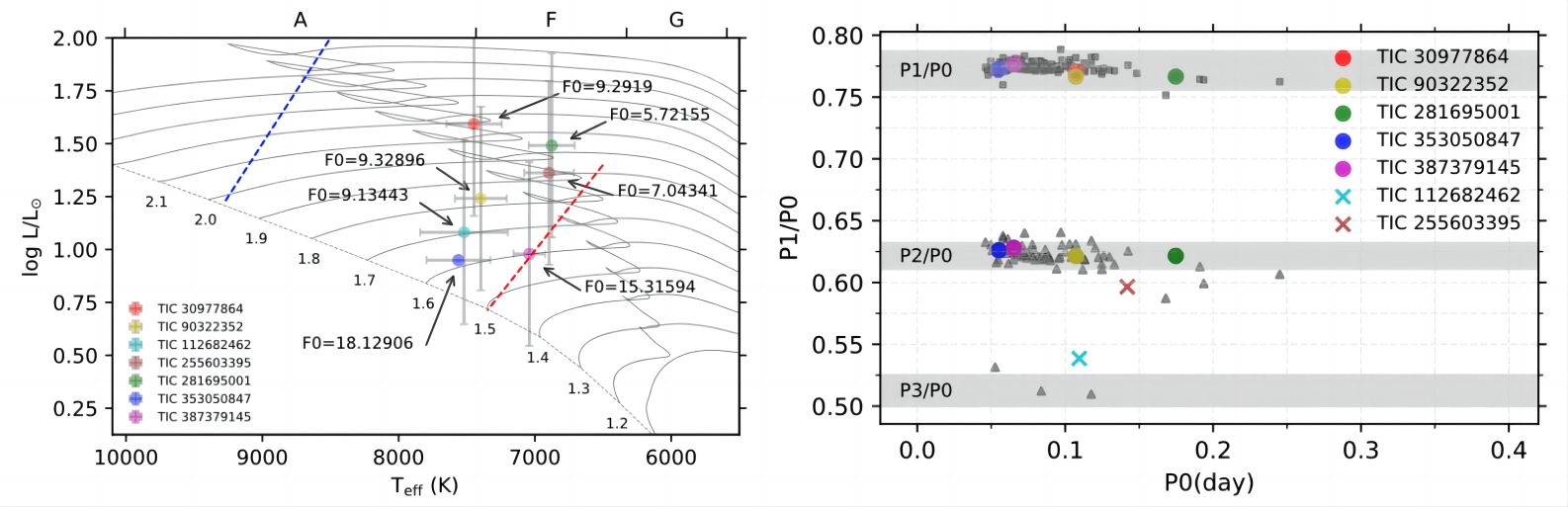
Fig 1 The left panel shows the positions of the 7 HADS on the Hierogram. The right panel shows the period ratio distribution of the 7 HADS.
Contact: LV Chenglong
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: lvchenglong@xao.ac.cn
Article link:https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/acf999
Attachment Download: