

The frequency-dependent periodic nulling and subpulse drifting properties in PSR J2048-1616
Using the archived observational data at 732, 1369 and 3100 MHz with the Parkes 64-m radio telescope, Dr. WEN Zhigang from Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory (XAO), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), along with his co-researchers from XAO and Xinjiang University, have performed a detailed study of single-pulse emission from a nearby, bright, and high-velocity pulsar J2048-1616.
The study was published in the Astrophysical Journal.
Pulse nulling and subpulse drifting are considered to be the most promising phenomena for uncovering the underlying physical processes. And the study of periodic behavior in pulse sequences has great significance in regards to understanding the geometry of the emission region.
In this study, the researchers found that this pulsar has a core-cone triple profile where the conal components show the presence of subpulse drifting in addition to the presence of quasiperiodic nulling across the entire profile. The periodic amplitude and phase modulations are presented with shorter periods in the trailing and leading components, respectively. The periodic modulation of nulls with a long period shows variations with time. The periodic modulations observed at multifrequencies of PSR J2048-1616 provided a further evidence that the periodic nulling originates due to different physical mechanisms compared to subpulse drifing.
The results of this research provided more insights into the periodic nulling and subpulse drifting from this pulsar.
“In order to reveal the physical mechanism of the periodic modulations, further long-term polarized single-pulse observations are required.” The authors of the paper expected.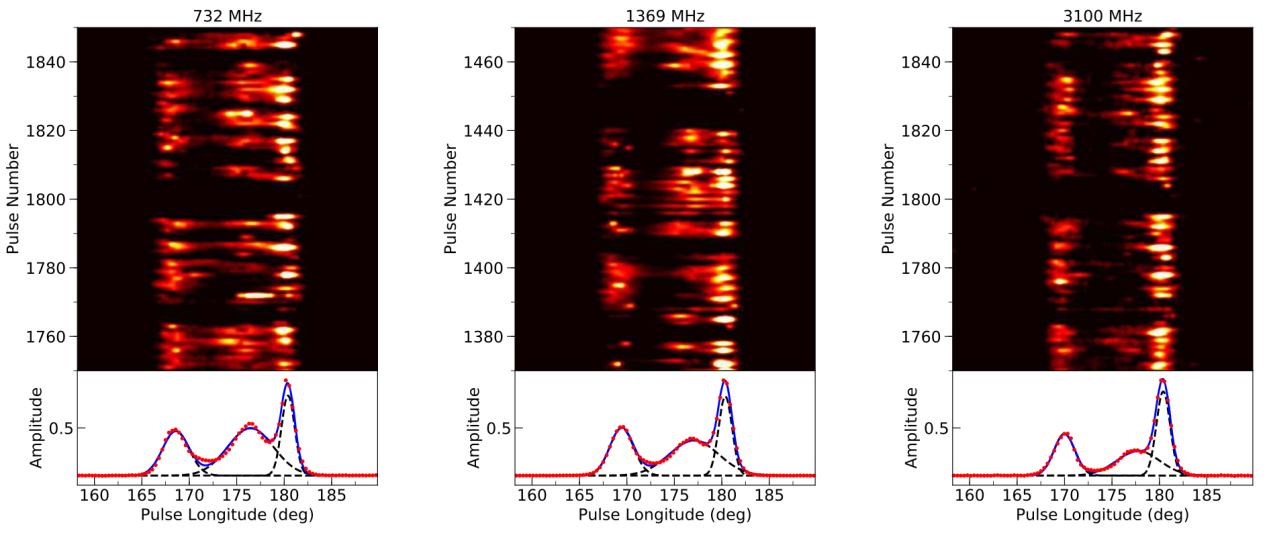
The color-map plots show the single-pulse sequences for PSR J2048-1616 at 732, 1369, and 3100 MHz, respectively.
Contact: Zhigang Wen
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: wenzhigang@xao.ac.cn
Article link: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/ac32ba
Attachment Download: