

Progress in Studies of High Velocity Type Ia supernova SN 2017hpa
Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) are widely believed to originate from thermonuclear runaway explosions of carbon-oxygen (CO) white dwarfs (WDs) in binary systems, and their essentially identical peak luminosities make them indicators of extragalactic distances and important probes for the study of cosmic expansion. There is a diversity of Type Ia supernovae, and different progenitor systems and explosion mechanisms may affect their accuracy as distance probes. Studies suggest that HV SN Ia and NV SN Ia may come from two different populations. Observational studies of Type Ia supernovae of different velocities contribute to the study of SN Ia diversity and provide insight into the explosion mechanism of SN Ia and their progenitor systems. Researchers from the Optical Astronomy Research Laboratory of Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory with their collaborators from domestic and abroad have confirmed that SN 2017fgc is a HV SN Ia with a photospheric expansion velocity of about 15000±150 km/s, which is significantly higher than that of a NV SN Ia. The results are published in the Astrophysical Journal (ApJ, 2021,919,49).
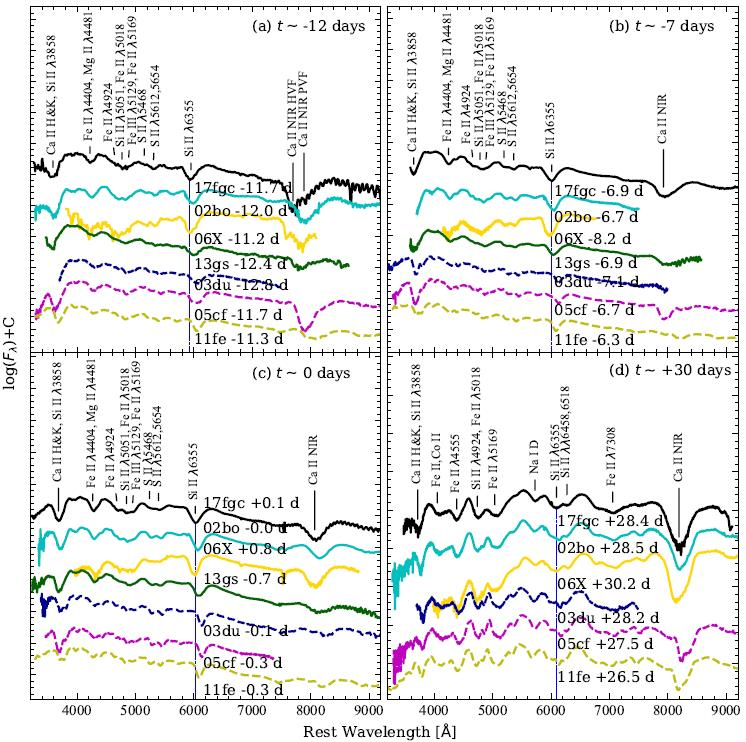
Figure 1: Comparison of different phase spectra of SN 2017fgc and well observed type Ia supernovae
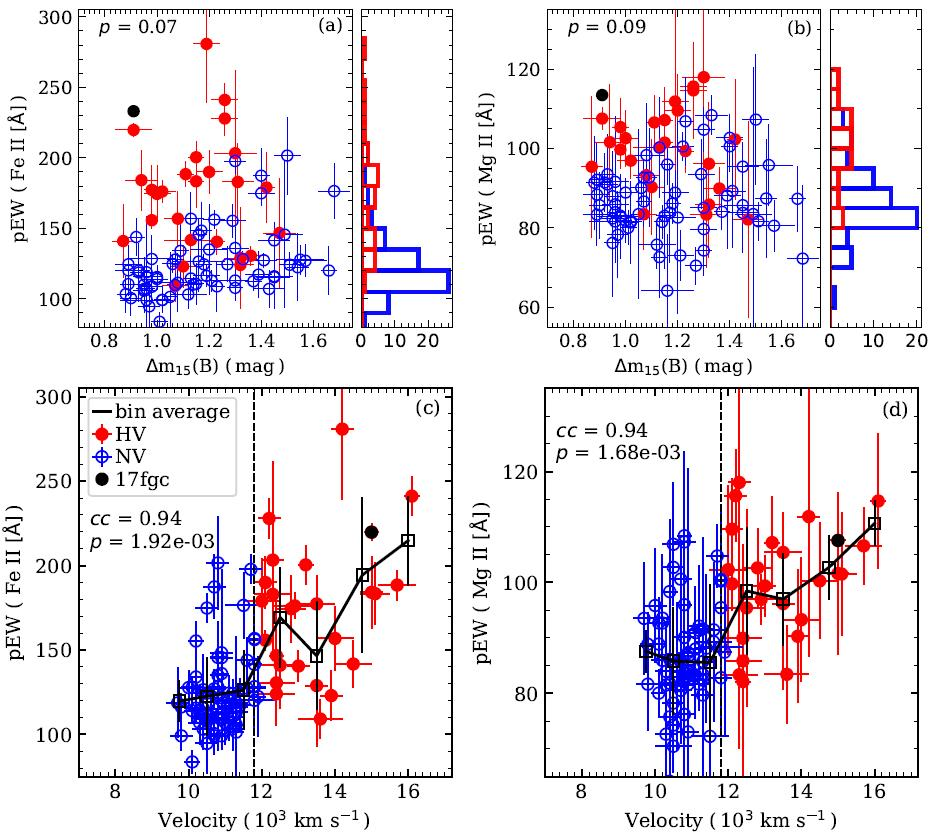
Figure 2: Scatter plot of the observed maximum light velocity of well observed type Ia supernovae and the equivalent width of Fe II blind lines and Mg II blind lines
Contact: ZENG Xiangyun
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: zengxiangyun@xao.ac.cn
Web: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2021ApJ...919...49Z/abstract
Attachment Download: