Orion Kleinmann-Low (Orion KL) nebula is the nearest massive star-forming region. An explosion occurred in this nebula about 550 years ago. The explosion not only accelerated several young stars, but also produced spectacular high velocity outflows. However, whether the dense gas in Orion KL is mainly heated by this explosion is under debate.
By analyzing the ALMA data, evidence that the dense gas is mainly heated by the explosion in Orion KL has been found by a recent work led by researchers from the group of star formation and evolution in Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, CAS. The gas kinetic temperature in Orion KL was derived based on the observed flux line ratios between different transitions of H2CS which is a thermometer of high density and high temperature gas. The resulting gas kinetic temperature values reach a maximum near the location of the explosive event and become lower farther away from it, indicating that the dense gas is heated by the shocks induced by the enigmatic explosive event. This has not been seen in such clarity before. The results have been published in The Astrophysical Journal (ApJ).
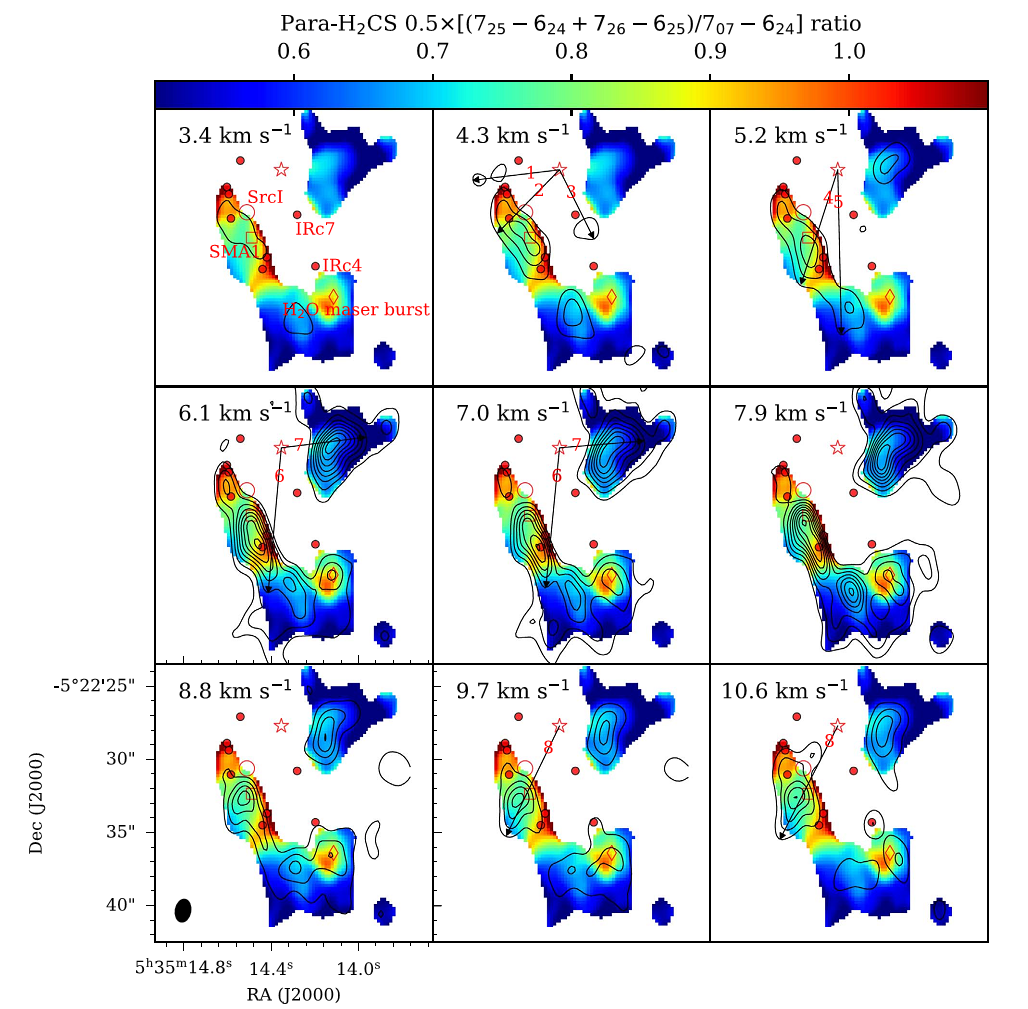
Color images represent the observed flux ratios of different transitions of H2CS; the higher ratios correspond to higher gas kinetic temperatures; the black contours represent the velocity integrated intensities of different velocities; the star represents the explosive center.
Contact: LI Dalei
Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Email: lidalei@xao.ac.cn
Article link: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/abae60