Muztagh-Ata One-point-nine-three-meter Synergy Telescope ( MOST)
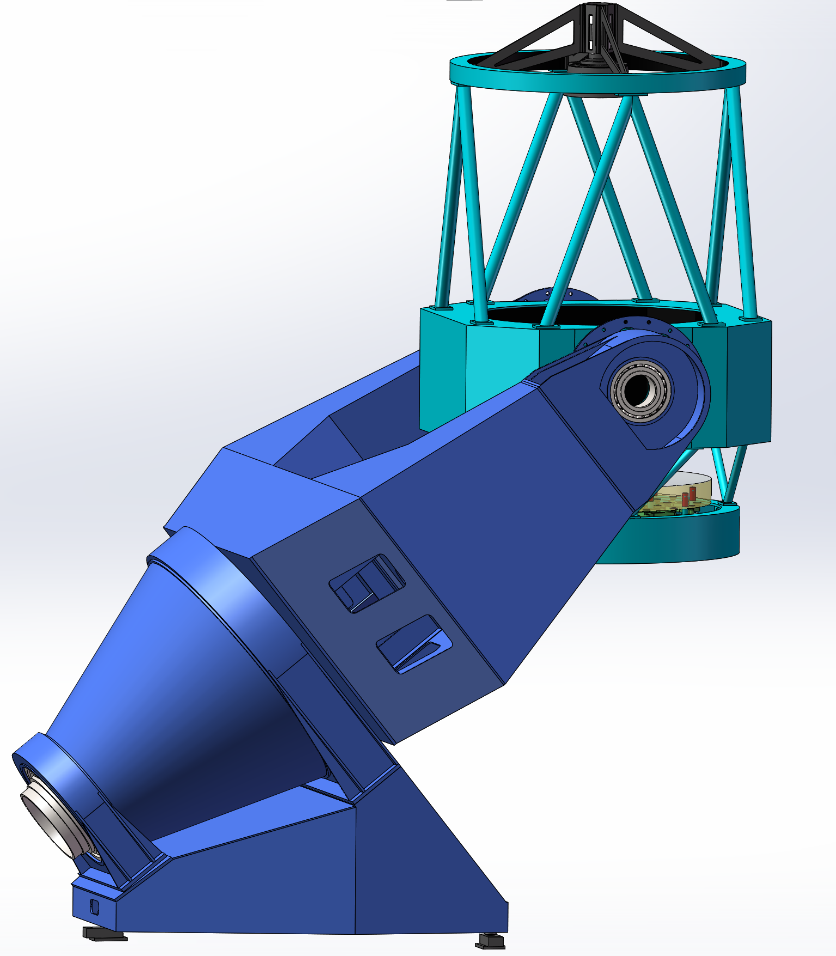
The Muztagh-Ata One-point-nine-three-meter Synergy Telescope (MOST), built at the Muztagh site in Xinjiang, is co-constructed by Beijing Normal University, Xinjiang Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanjing Institute of Astronomical Optics & Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Xinjiang University. This optical telescope adopts a remote-controlled, fully automated observation mode. It is planned to be equipped with multi-color photometry/imaging and medium-to-low dispersion spectroscopic observation instruments. It is positioned as a high-precision photometric, astrometric, and general-purpose telescope to fully utilize the advantages of the Muztagh site, which include excellent seeing conditions, dark sky brightness, and high transmission rates at both red and blue ends of the spectrum. The telescope will be dedicated to research in various fields, including time-domain transients, electromagnetic counterparts of gravitational waves, supernovae and their progenitor stars, variable stars, active galactic nuclei, star clusters, exoplanets, and near-Earth objects.

